Element: mouseenter event
Baseline
Widely available
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015.
The mouseenter event is fired at an Element when a pointing device (usually a mouse) is initially moved so that its hotspot is within the element at which the event was fired.
Note that "moving into an element" refers to the element's position in the DOM tree, not to its visual position. For example, if a child element is positioned so it is placed outside its parent, then moving into the child element will trigger mouseenter on the parent element, even though the pointer is still outside the bounds of the parent element.
Syntax
Use the event name in methods like addEventListener(), or set an event handler property.
addEventListener("mouseenter", (event) => { })
onmouseenter = (event) => { }
Event type
A MouseEvent. Inherits from UIEvent and Event.
Event properties
This interface also inherits properties of its parents, UIEvent and Event.
MouseEvent.altKeyRead only-
Returns
trueif the alt key was down when the mouse event was fired. -
The button number that was pressed (if applicable) when the mouse event was fired.
-
The buttons being pressed (if any) when the mouse event was fired.
MouseEvent.clientXRead only-
The X coordinate of the mouse pointer in viewport coordinates.
MouseEvent.clientYRead only-
The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer in viewport coordinates.
MouseEvent.ctrlKeyRead only-
Returns
trueif the control key was down when the mouse event was fired. MouseEvent.layerXNon-standard Read only-
Returns the horizontal coordinate of the event relative to the current layer.
MouseEvent.layerYNon-standard Read only-
Returns the vertical coordinate of the event relative to the current layer.
MouseEvent.metaKeyRead only-
Returns
trueif the meta key was down when the mouse event was fired. MouseEvent.movementXRead only-
The X coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the position of the last
mousemoveevent. MouseEvent.movementYRead only-
The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the position of the last
mousemoveevent. MouseEvent.offsetXRead only-
The X coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the position of the padding edge of the target node.
MouseEvent.offsetYRead only-
The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the position of the padding edge of the target node.
MouseEvent.pageXRead only-
The X coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the whole document.
MouseEvent.pageYRead only-
The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the whole document.
-
The secondary target for the event, if there is one.
MouseEvent.screenXRead only-
The X coordinate of the mouse pointer in screen coordinates.
MouseEvent.screenYRead only-
The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer in screen coordinates.
MouseEvent.shiftKeyRead only-
Returns
trueif the shift key was down when the mouse event was fired. MouseEvent.mozInputSourceNon-standard Read only-
The type of device that generated the event (one of the
MOZ_SOURCE_*constants). This lets you, for example, determine whether a mouse event was generated by an actual mouse or by a touch event (which might affect the degree of accuracy with which you interpret the coordinates associated with the event). MouseEvent.webkitForceNon-standard Read only-
The amount of pressure applied when clicking.
MouseEvent.xRead only-
Alias for
MouseEvent.clientX. MouseEvent.yRead only-
Alias for
MouseEvent.clientY.
Usage notes
Though similar to mouseover, mouseenter differs in that it doesn't bubble and it isn't sent to any descendants when the pointer is moved from one of its descendants' physical space to its own physical space. Other than that, enter and over events for the same situation are dispatched at the same time, if appropriate.
Behavior of mouseenter events
This describes the mouseenter events received by each of four concentric divs with no padding or margin, so the events all happen at the same time:
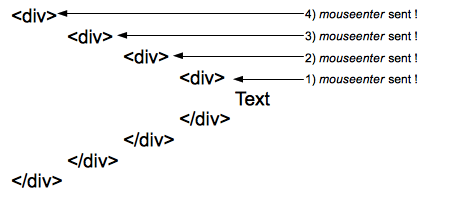 One
One mouseenter event is sent to each element of the hierarchy when entering them. Here 4 events are sent to the four elements of the hierarchy when the pointer reaches the text.
Behavior of mouseover events
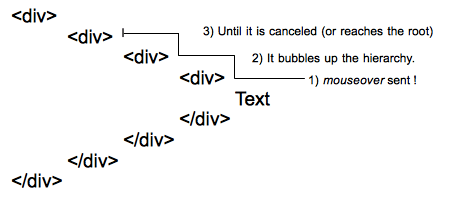 A single
A single mouseover event is sent to the deepest element of the DOM tree, then it bubbles up the hierarchy until it is canceled by a handler or reaches the root.
With deep hierarchies, the number of mouseenter events sent can be quite huge and cause significant performance problems. In such cases, it is better to listen for mouseover events.
Combined with the corresponding mouseleave (which is fired at the element when the mouse exits its content area), the mouseenter event acts in a very similar way to the CSS :hover pseudo-class.
Examples
The mouseover documentation has an example illustrating the difference between mouseover and mouseenter.
mouseenter
The following trivial example uses the mouseenter event to change the border on the div when the mouse enters the space allotted to it. It then adds an item to the list with the number of the mouseenter or mouseleave event.
HTML
<div id="mouseTarget">
<ul id="unorderedList">
<li>No events yet!</li>
</ul>
</div>
CSS
Styling the div to make it more visible.
#mouseTarget {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 15rem;
border: 1px solid #333333;
}
JavaScript
let enterEventCount = 0;
let leaveEventCount = 0;
const mouseTarget = document.getElementById("mouseTarget");
const unorderedList = document.getElementById("unorderedList");
mouseTarget.addEventListener("mouseenter", (e) => {
mouseTarget.style.border = "5px dotted orange";
enterEventCount++;
addListItem(`This is mouseenter event ${enterEventCount}.`);
});
mouseTarget.addEventListener("mouseleave", (e) => {
mouseTarget.style.border = "1px solid #333333";
leaveEventCount++;
addListItem(`This is mouseleave event ${leaveEventCount}.`);
});
function addListItem(text) {
// Create a new text node using the supplied text
const newTextNode = document.createTextNode(text);
// Create a new li element
const newListItem = document.createElement("li");
// Add the text node to the li element
newListItem.appendChild(newTextNode);
// Add the newly created list item to list
unorderedList.appendChild(newListItem);
}
Result
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| UI Events # event-type-mouseenter |
| HTML # handler-onmouseenter |