<script>: The Script element
Baseline
Widely available
*
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015.
* Some parts of this feature may have varying levels of support.
The <script> HTML element is used to embed executable code or data; this is typically used to embed or refer to JavaScript code. The <script> element can also be used with other languages, such as WebGL's GLSL shader programming language and JSON.
Attributes
This element includes the global attributes.
async-
For classic scripts, if the
asyncattribute is present, then the classic script will be fetched in parallel to parsing and evaluated as soon as it is available.For module scripts, if the
asyncattribute is present then the scripts and all their dependencies will be fetched in parallel to parsing and evaluated as soon as they are available.Warning: This attribute must not be used if the
srcattribute is absent (i.e., for inline scripts) for classic scripts, in this case it would have no effect.This attribute allows the elimination of parser-blocking JavaScript where the browser would have to load and evaluate scripts before continuing to parse.
deferhas a similar effect in this case.If the attribute is specified with the
deferattribute, the element will act as if only theasyncattribute is specified.This is a boolean attribute: the presence of a boolean attribute on an element represents the true value, and the absence of the attribute represents the false value.
See Browser compatibility for notes on browser support. See also Async scripts for asm.js.
attributionsrcDeprecated-
Specifies that you want the browser to send an
Attribution-Reporting-Eligibleheader along with the script resource request. On the server-side this is used to trigger sending anAttribution-Reporting-Register-SourceorAttribution-Reporting-Register-Triggerheader in the response, to register a JavaScript-based attribution source or attribution trigger, respectively. Which response header should be sent back depends on the value of theAttribution-Reporting-Eligibleheader that triggered the registration.Note: Alternatively, JavaScript-based attribution sources or triggers can be registered by sending a
fetch()request containing theattributionReportingoption (either set directly on thefetch()call or on aRequestobject passed into thefetch()call), or by sending anXMLHttpRequestwithsetAttributionReporting()invoked on the request object.There are two versions of this attribute that you can set:
-
Boolean, i.e., just the
attributionsrcname. This specifies that you want theAttribution-Reporting-Eligibleheader sent to the same server as thesrcattribute points to. This is fine when you are handling the attribution source or trigger registration on the same server. When registering an attribution trigger this property is optional, and an empty string value will be used if it is omitted. -
Value containing one or more URLs, for example:
html<script src="myscript.js" attributionsrc="https://a.example/register-source https://b.example/register-source"></script>This is useful in cases where the requested resource is not on a server you control, or you just want to handle registering the attribution source on a different server. In this case, you can specify one or more URLs as the value of
attributionsrc. When the resource request occurs theAttribution-Reporting-Eligibleheader will be sent to the URL(s) specified inattributionSrcin addition to the resource origin. These URLs can then respond with anAttribution-Reporting-Register-SourceorAttribution-Reporting-Register-Triggerheader as appropriate to complete registration.Note: Specifying multiple URLs means that multiple attribution sources can be registered on the same feature. You might for example have different campaigns that you are trying to measure the success of, which involve generating different reports on different data.
See the Attribution Reporting API for more details.
-
blocking-
This attribute explicitly indicates that certain operations should be blocked until the script has executed. The operations that are to be blocked must be a space-separated list of blocking tokens. Currently there is only one token:
render: The rendering of content on the screen is blocked.
Note: Only
scriptelements in the document's<head>can possibly block rendering. Scripts are not render-blocking by default; if ascriptelement does not includetype="module",async, ordefer, then it blocks parsing, not rendering. If such ascriptelement is added dynamically via script, you must setblocking = "render"for it to block rendering. crossorigin-
Normal
scriptelements pass minimal information to thewindow.onerrorfor scripts which do not pass the standard CORS checks. To allow error logging for sites which use a separate domain for static media, use this attribute. See CORS settings attributes for a more descriptive explanation of its valid arguments. defer-
This Boolean attribute is set to indicate to a browser that the script is meant to be executed after the document has been parsed, but before firing
DOMContentLoadedevent.Scripts with the
deferattribute will prevent theDOMContentLoadedevent from firing until the script has loaded and finished evaluating.Warning: This attribute must not be used if the
srcattribute is absent (i.e., for inline scripts), in this case it would have no effect.The
deferattribute has no effect on module scripts — they defer by default.Scripts with the
deferattribute will execute in the order in which they appear in the document.This attribute allows the elimination of parser-blocking JavaScript where the browser would have to load and evaluate scripts before continuing to parse.
asynchas a similar effect in this case.If the attribute is specified with the
asyncattribute, the element will act as if only theasyncattribute is specified. fetchpriority-
Provides a hint of the relative priority to use when fetching an external script. Allowed values:
integrity-
This attribute contains inline metadata that a user agent can use to verify that a fetched resource has been delivered without unexpected manipulation. The attribute must not be specified when the
srcattribute is absent. See Subresource Integrity. nomodule-
This Boolean attribute is set to indicate that the script should not be executed in browsers that support ES modules — in effect, this can be used to serve fallback scripts to older browsers that do not support modular JavaScript code.
nonce-
A cryptographic nonce (number used once) to allow scripts in a script-src Content-Security-Policy. The server must generate a unique nonce value each time it transmits a policy. It is critical to provide a nonce that cannot be guessed as bypassing a resource's policy is otherwise trivial.
referrerpolicy-
Indicates which referrer to send when fetching the script, or resources fetched by the script:
no-referrer: TheRefererheader will not be sent.no-referrer-when-downgrade: TheRefererheader will not be sent to origins without TLS (HTTPS).origin: The sent referrer will be limited to the origin of the referring page: its scheme, host, and port.origin-when-cross-origin: The referrer sent to other origins will be limited to the scheme, the host, and the port. Navigations on the same origin will still include the path.same-origin: A referrer will be sent for same origin, but cross-origin requests will contain no referrer information.strict-origin: Only send the origin of the document as the referrer when the protocol security level stays the same (HTTPS→HTTPS), but don't send it to a less secure destination (HTTPS→HTTP).strict-origin-when-cross-origin(default): Send a full URL when performing a same-origin request, only send the origin when the protocol security level stays the same (HTTPS→HTTPS), and send no header to a less secure destination (HTTPS→HTTP).unsafe-url: The referrer will include the origin and the path (but not the fragment, password, or username). This value is unsafe, because it leaks origins and paths from TLS-protected resources to insecure origins.
Note: An empty string value (
"") is both the default value, and a fallback value ifreferrerpolicyis not supported. Ifreferrerpolicyis not explicitly specified on the<script>element, it will adopt a higher-level referrer policy, i.e., one set on the whole document or domain. If a higher-level policy is not available, the empty string is treated as being equivalent tostrict-origin-when-cross-origin. src-
This attribute specifies the URI of an external script; this can be used as an alternative to embedding a script directly within a document.
type-
This attribute indicates the type of script represented. The value of this attribute will be one of the following:
- Attribute is not set (default), an empty string, or a JavaScript MIME type
-
Indicates that the script is a "classic script", containing JavaScript code. Authors are encouraged to omit the attribute if the script refers to JavaScript code rather than specify a MIME type. JavaScript MIME types are listed in the IANA media types specification.
importmap-
This value indicates that the body of the element contains an import map. The import map is a JSON object that developers can use to control how the browser resolves module specifiers when importing JavaScript modules.
module-
This value causes the code to be treated as a JavaScript module. The processing of the script contents is deferred. The
charsetanddeferattributes have no effect. For information on usingmodule, see our JavaScript modules guide. Unlike classic scripts, module scripts require the use of the CORS protocol for cross-origin fetching. speculationrulesExperimental-
This value indicates that the body of the element contains speculation rules. Speculation rules take the form of a JSON object that determine what resources should be prefetched or prerendered by the browser. This is part of the Speculation Rules API.
- Any other value
-
The embedded content is treated as a data block, and won't be processed by the browser. Developers must use a valid MIME type that is not a JavaScript MIME type to denote data blocks. All of the other attributes will be ignored, including the
srcattribute.
Deprecated attributes
charsetDeprecated-
If present, its value must be an ASCII case-insensitive match for
utf-8. It's unnecessary to specify thecharsetattribute, because documents must use UTF-8, and thescriptelement inherits its character encoding from the document. languageDeprecated Non-standard-
Like the
typeattribute, this attribute identifies the scripting language in use. Unlike thetypeattribute, however, this attribute's possible values were never standardized. Thetypeattribute should be used instead.
Notes
Scripts without async, defer or type="module" attributes, as well as inline scripts without the type="module" attribute, are fetched and executed immediately before the browser continues to parse the page.
The script should be served with the text/javascript MIME type, but browsers are lenient and only block them if the script is served with an image type (image/*), a video type (video/*), an audio type (audio/*), or text/csv.
If the script is blocked, an error event is sent to the element; otherwise, a load event is sent.
Examples
Basic usage
This example shows how to import (an external) script using the <script> element:
<script src="javascript.js"></script>
The following example shows how to put (an inline) script inside the <script> element:
<script>
alert("Hello World!");
</script>
async and defer
Scripts loaded using the async attribute will download the script without blocking the page while the script is being fetched.
However, once the download is complete, the script will execute, which blocks the page from rendering. This means that the rest of the content on the web page is prevented from being processed and displayed to the user until the script finishes executing.
You get no guarantee that scripts will run in any specific order.
It is best to use async when the scripts in the page run independently from each other and depend on no other script on the page.
Scripts loaded with the defer attribute will load in the order they appear on the page.
They won't run until the page content has all loaded, which is useful if your scripts depend on the DOM being in place (e.g., they modify one or more elements on the page).
Here is a visual representation of the different script loading methods and what that means for your page:
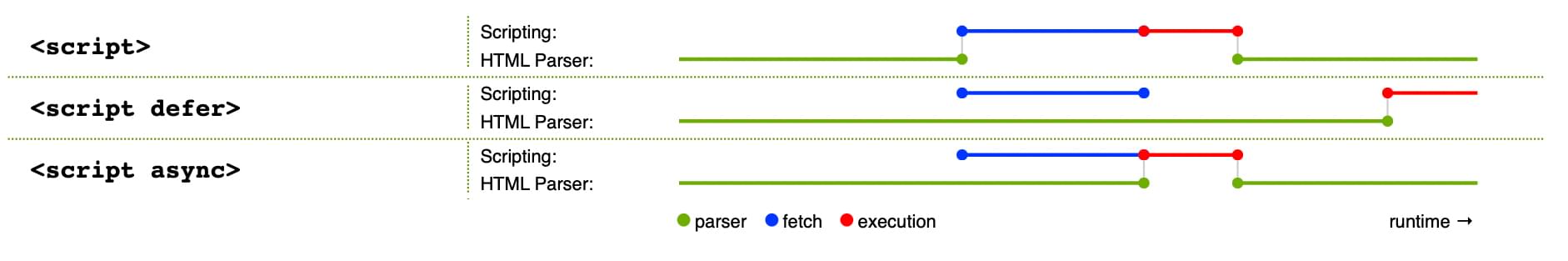
This image is from the HTML spec, copied and cropped to a reduced version, under CC BY 4.0 license terms.
For example, if you have the following script elements:
<script async src="js/vendor/jquery.js"></script>
<script async src="js/script2.js"></script>
<script async src="js/script3.js"></script>
You can't rely on the order the scripts will load in.
jquery.js may load before or after script2.js and script3.js and if this is the case, any functions in those scripts depending on jquery will produce an error because jquery will not be defined at the time the script runs.
async should be used when you have a bunch of background scripts to load in, and you just want to get them in place as soon as possible.
For example, maybe you have some game data files to load, which will be needed when the game actually begins, but for now you just want to get on with showing the game intro, titles, and lobby, without them being blocked by script loading.
Scripts loaded using the defer attribute (see below) will run in the order they appear in the page and execute them as soon as the script and content are downloaded:
<script defer src="js/vendor/jquery.js"></script>
<script defer src="js/script2.js"></script>
<script defer src="js/script3.js"></script>
In the second example, we can be sure that jquery.js will load before script2.js and script3.js and that script2.js will load before script3.js.
They won't run until the page content has all loaded, which is useful if your scripts depend on the DOM being in place (e.g., they modify one or more elements on the page).
To summarize:
asyncanddeferboth instruct the browser to download the script(s) in a separate thread, while the rest of the page (the DOM, etc.) is downloading, so the page loading is not blocked during the fetch process.- scripts with an
asyncattribute will execute as soon as the download is complete. This blocks the page and does not guarantee any specific execution order. - scripts with a
deferattribute will load in the order they are in and will only execute once everything has finished loading. - If your scripts should be run immediately and they don't have any dependencies, then use
async. - If your scripts need to wait for parsing and depend on other scripts and/or the DOM being in place, load them using
deferand put their corresponding<script>elements in the order you want the browser to execute them.
Module fallback
Browsers that support the module value for the type attribute ignore any script with a nomodule attribute. That enables you to use module scripts while providing nomodule-marked fallback scripts for non-supporting browsers.
<script type="module" src="main.js"></script>
<script nomodule src="fallback.js"></script>
Importing modules with importmap
When importing modules in scripts, if you don't use the type=importmap feature, then each module must be imported using a module specifier that is either an absolute or relative URL.
In the example below, the first module specifier is an absolute URL, while the second ("./shapes/square.js") resolves relative to the base URL of the document.
import { name as circleName } from "https://example.com/shapes/circle.js";
import { name as squareName, draw } from "./shapes/square.js";
An import map allows you to provide a mapping that, if matched, can replace the text in the module specifier.
The import map below defines keys circle and square that can be used as aliases for the module specifiers shown above.
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"circle": "https://example.com/shapes/circle.js",
"square": "./shapes/square.js"
}
}
</script>
This allows us to import modules using names in the module specifier (rather than absolute or relative URLs).
import { name as circleName } from "circle";
import { name as squareName, draw } from "square";
For more examples of what you can do with import maps, see the Importing modules using import maps section in the JavaScript modules guide.
Embedding data in HTML
You can also use the <script> element to embed data in HTML with server-side rendering by specifying a valid non-JavaScript MIME type in the type attribute.
<!-- Generated by the server -->
<script id="data" type="application/json">
{
"userId": 1234,
"userName": "Maria Cruz",
"memberSince": "2000-01-01T00:00:00.000Z"
}
</script>
<!-- Static -->
<script>
const userInfo = JSON.parse(document.getElementById("data").text);
console.log("User information: %o", userInfo);
</script>
Blocking rendering till a script is fetched and executed
You can include render token inside a blocking attribute;
the rendering of the page will be blocked till the script is fetched and executed. In the example below, we block rendering on an async script,
so that the script doesn't block parsing but is guaranteed to be evaluated before rendering starts.
<script blocking="render" async src="async-script.js"></script>
Technical summary
| Content categories | Metadata content, Flow content, Phrasing content. |
|---|---|
| Permitted content | Dynamic script such as text/javascript. |
| Tag omission | None, both the starting and ending tag are mandatory. |
| Permitted parents | Any element that accepts metadata content, or any element that accepts phrasing content. |
| Implicit ARIA role | No corresponding role |
| Permitted ARIA roles | No role permitted |
| DOM interface | HTMLScriptElement |
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| HTML # the-script-element |