Document Object Model (DOM)
The Document Object Model (DOM) connects web pages to scripts or programming languages by representing the structure of a document—such as the HTML representing a web page—in memory. Usually it refers to JavaScript, even though modeling HTML, SVG, or XML documents as objects are not part of the core JavaScript language.
The DOM represents a document with a logical tree. Each branch of the tree ends in a node, and each node contains objects. DOM methods allow programmatic access to the tree. With them, you can change the document's structure, style, or content.
Nodes can also have event handlers attached to them. Once an event is triggered, the event handlers get executed.
Concepts and usage
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for web documents. It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style, and content. The DOM represents the document as nodes and objects; that way, programming languages can interact with the page.
A web page is a document that can be either displayed in the browser window or as the HTML source. In both cases, it is the same document but the Document Object Model (DOM) representation allows it to be manipulated. As an object-oriented representation of the web page, it can be modified with a scripting language such as JavaScript.
For example, the DOM specifies that the querySelectorAll method in this code snippet must return a list of all the <p> elements in the document:
const paragraphs = document.querySelectorAll("p");
// paragraphs[0] is the first <p> element
// paragraphs[1] is the second <p> element, etc.
alert(paragraphs[0].nodeName);
All of the properties, methods, and events available for manipulating and creating web pages are organized into objects. For example, the document object that represents the document itself, any table objects that implement the HTMLTableElement DOM interface for accessing HTML tables, and so forth, are all objects.
The DOM is built using multiple APIs that work together. The core DOM defines the entities describing any document and the objects within it. This is expanded upon as needed by other APIs that add new features and capabilities to the DOM. For example, the HTML DOM API adds support for representing HTML documents to the core DOM, and the SVG API adds support for representing SVG documents.
What is a DOM tree?
A DOM tree is a tree structure whose nodes represent an HTML or XML document's contents. Each HTML or XML document has a DOM tree representation. For example, consider the following document:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>My Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Header</h1>
<p>Paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
It has a DOM tree that looks like this:
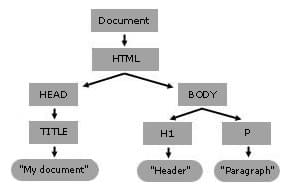
Although the above tree is similar to the above document's DOM tree, they're not identical, as the actual DOM tree preserves whitespace.
When a web browser parses an HTML document, it builds a DOM tree and then uses it to display the document.
DOM and JavaScript
The previous short example, like nearly all examples, is JavaScript. That is to say, it is written in JavaScript, but uses the DOM to access the document and its elements. The DOM is not a programming language, but without it, the JavaScript language wouldn't have any model or notion of web pages, HTML documents, SVG documents, and their component parts. The document as a whole, the head, tables within the document, table headers, text within the table cells, and all other elements in a document are parts of the document object model for that document. They can all be accessed and manipulated using the DOM and a scripting language like JavaScript.
The DOM is not part of the JavaScript language, but is instead a Web API used to build websites. JavaScript can also be used in other contexts. For example, Node.js runs JavaScript programs on a computer, but provides a different set of APIs, and the DOM API is not a core part of the Node.js runtime.
The DOM was designed to be independent of any particular programming language, making the structural representation of the document available from a single, consistent API. Even if most web developers will only use the DOM through JavaScript, implementations of the DOM can be built for any language, as this Python example demonstrates:
# Python DOM example
import xml.dom.minidom as m
doc = m.parse(r"C:\Projects\Py\chap1.xml")
doc.nodeName # DOM property of document object
p_list = doc.getElementsByTagName("para")
For more information on what technologies are involved in writing JavaScript on the web, see JavaScript technologies overview.
Accessing the DOM
You don't have to do anything special to begin using the DOM. You use the API directly in JavaScript from within what is called a script, a program run by a browser.
When you create a script, whether inline in a <script> element or included in the web page, you can immediately begin using the API for the document or window objects to manipulate the document itself, or any of the various elements in the web page (the descendant elements of the document). Your DOM programming may be something as simple as the following example, which displays a message on the console by using the console.log() function:
<body onload="console.log('Welcome to my home page!');">
…
</body>
As it is generally not recommended to mix the structure of the page (written in HTML) and manipulation of the DOM (written in JavaScript), the JavaScript parts will be grouped together here, and separated from the HTML.
For example, the following function creates a new h1 element, adds text to that element, and then adds it to the tree for the document:
<html lang="en">
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
// create a couple of elements in an otherwise empty HTML page
const heading = document.createElement("h1");
const headingText = document.createTextNode("Big Head!");
heading.appendChild(headingText);
document.body.appendChild(heading);
</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM interfaces
The following are all interfaces defined by the DOM specification:
AbortControllerAbortSignalAbstractRangeAttrCDATASectionCharacterDataCommentCustomEventDocumentDocumentFragmentDocumentTypeDOMErrorDeprecatedDOMExceptionDOMImplementationDOMParserDOMTokenListElementEventEventTargetHTMLCollectionMutationObserverMutationRecordNamedNodeMapNodeNodeIteratorNodeListProcessingInstructionQuotaExceededErrorRangeShadowRootStaticRangeTextTreeWalkerXMLDocumentXPathEvaluatorXPathExpressionXPathResultXSLTProcessor
This guide is about the objects and the actual things you can use to manipulate the DOM hierarchy. There are many points where understanding how these work can be confusing. For example, the object representing the HTML form element gets its name property from the HTMLFormElement interface but its className property from the HTMLElement interface. In both cases, the property you want is in that form object.
But the relationship between objects and the interfaces that they implement in the DOM can be confusing, and so this section attempts to say a little something about the actual interfaces in the DOM specification and how they are made available.
Interfaces and objects
Many objects implement several different interfaces. The table object, for example, implements a specialized HTMLTableElement interface, which includes such methods as createCaption and insertRow. But since it's also an HTML element, table implements the Element interface described in the DOM Element Reference chapter. And finally, since an HTML element is also, as far as the DOM is concerned, a node in the tree of nodes that make up the object model for an HTML or XML page, the table object also implements the more basic Node interface, from which Element derives.
When you get a reference to a table object, as in the following example, you routinely use all three of these interfaces interchangeably on the object, perhaps without knowing it.
const table = document.getElementById("table");
const tableAttrs = table.attributes; // Node/Element interface
for (const attr of tableAttrs) {
// HTMLTableElement interface: border attribute
if (attr.nodeName.toLowerCase() === "border") {
table.border = "1";
}
}
// HTMLTableElement interface: summary attribute
table.summary = "note: increased border";
Fundamental data types
This page tries to describe the various objects and types in simple terms. But there are a number of different data types being passed around the API that you should be aware of.
Note: Because the vast majority of code that uses the DOM revolves around manipulating HTML documents, it's common to refer to the nodes in the DOM as elements, although strictly speaking not every node is an element.
The following table briefly describes these data types.
| Data type (Interface) | Description |
|---|---|
Document |
When a member returns an object of type document (e.g., the
ownerDocument property of an element returns the
document to which it belongs), this object is the root
document object itself. The
DOM document Reference
chapter describes the document object.
|
Node |
Every object located within a document is a node of some kind. In an HTML document, an object can be an element node but also a text node or attribute node. |
Element |
The element type is based on node. It refers
to an element or a node of type element returned by a
member of the DOM API. Rather than saying, for example, that the
document.createElement() method returns an
object reference to a node, we just say that this method
returns the element that has just been created in the DOM.
element objects implement the DOM
Element interface and also the more basic
Node interface, both of which are included together in this
reference. In an HTML document, elements are further enhanced by the
HTML DOM API's HTMLElement interface as well as
other interfaces describing capabilities of specific kinds of elements
(for instance, HTMLTableElement for
<table> elements).
|
Attr |
When an attribute is returned by a member (e.g., by the
createAttribute() method), it is an object reference that
exposes a special (albeit small) interface for attributes. Attributes
are nodes in the DOM just like elements are, though you may rarely use
them as such.
|
There are also some common terminology considerations to keep in mind. It's common to refer to any Attr node as an attribute, for example, and to refer to an array of DOM nodes as a nodeList. You'll find these terms and others to be introduced and used throughout the documentation.
The document and window objects are the objects whose interfaces you generally use most often in DOM programming. In simple terms, the window object represents something like the browser, and the document object is the root of the document itself. Element inherits from the generic Node interface, and together these two interfaces provide many of the methods and properties you use on individual elements. These elements may also have specific interfaces for dealing with the kind of data those elements hold, as in the table object example in the previous section.
Obsolete DOM interfaces
The Document Object Model has been highly simplified. To achieve this, the following interfaces in the different DOM level 3 or earlier specifications have been removed. They are no longer available to web developers.
DOMConfigurationDOMErrorHandlerDOMImplementationListDOMImplementationRegistryDOMImplementationSourceDOMLocatorDOMObjectDOMSettableTokenListDOMUserDataElementTraversalEntityEntityReferenceNameListNotationTypeInfoUserDataHandler
HTML DOM
A document containing HTML is described using the Document interface, which is extended by the HTML specification to include various HTML-specific features. In particular, the Element interface is enhanced to become HTMLElement and various subclasses, each representing one of (or a family of closely related) elements.
The HTML DOM API provides access to various browser features such as tabs and windows, CSS styles and stylesheets, browser history, etc. These interfaces are discussed further in the HTML DOM API documentation.
SVG DOM
Similarly, a document containing SVG is also described using the Document interface, which is extended by the SVG specification to include various SVG-specific features. In particular, the Element interface is enhanced to become SVGElement and various subclasses, each representing an element or a family of closely related elements. These interfaces are discussed further in the SVG API documentation.
Examples
Setting text content
This example uses a <div> element containing a <textarea> and two <button> elements. When the user clicks the first button we set some text in the <textarea>. When the user clicks the second button we clear the text. We use:
Document.querySelector()to access the<textarea>and the buttonEventTarget.addEventListener()to listen for button clicksNode.textContentto set and clear the text.
HTML
<div class="container">
<textarea class="story"></textarea>
<button id="set-text" type="button">Set text content</button>
<button id="clear-text" type="button">Clear text content</button>
</div>
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
gap: 0.5rem;
flex-direction: column;
}
button {
width: 200px;
}
JavaScript
const story = document.body.querySelector(".story");
const setText = document.body.querySelector("#set-text");
setText.addEventListener("click", () => {
story.textContent = "It was a dark and stormy night...";
});
const clearText = document.body.querySelector("#clear-text");
clearText.addEventListener("click", () => {
story.textContent = "";
});
Result
Adding a child element
This example uses a <div> element containing a <div> and two <button> elements. When the user clicks the first button we create a new element and add it as a child of the <div>. When the user clicks the second button we remove the child element. We use:
Document.querySelector()to access the<div>and the buttonsEventTarget.addEventListener()to listen for button clicksDocument.createElementto create the elementNode.appendChild()to add the childNode.removeChild()to remove the child.
HTML
<div class="container">
<div class="parent">parent</div>
<button id="add-child" type="button">Add a child</button>
<button id="remove-child" type="button">Remove child</button>
</div>
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
gap: 0.5rem;
flex-direction: column;
}
button {
width: 100px;
}
div.parent {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 5px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
div.child {
border: 1px solid red;
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
width: 80px;
height: 60px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
JavaScript
const parent = document.body.querySelector(".parent");
const addChild = document.body.querySelector("#add-child");
addChild.addEventListener("click", () => {
// Only add a child if we don't already have one
// in addition to the text node "parent"
if (parent.childNodes.length > 1) {
return;
}
const child = document.createElement("div");
child.classList.add("child");
child.textContent = "child";
parent.appendChild(child);
});
const removeChild = document.body.querySelector("#remove-child");
removeChild.addEventListener("click", () => {
const child = document.body.querySelector(".child");
parent.removeChild(child);
});
Result
Reading and modifying the tree
Suppose the author wants to change the header of the document in What is a DOM tree? and write two paragraphs instead of one. The following script would do the job:
HTML
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>My Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="Change this document." />
<h2>Header</h2>
<p>Paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript
document.querySelector("input").addEventListener("click", () => {
// document.getElementsByTagName("h2") returns a NodeList of the <h2>
// elements in the document, and the first is number 0:
const header = document.getElementsByTagName("h2").item(0);
// The firstChild of the header is a Text node:
header.firstChild.data = "A dynamic document";
// Now header is "A dynamic document".
// Access the first paragraph
const para = document.getElementsByTagName("p").item(0);
para.firstChild.data = "This is the first paragraph.";
// Create a new Text node for the second paragraph
const newText = document.createTextNode("This is the second paragraph.");
// Create a new Element to be the second paragraph
const newElement = document.createElement("p");
// Put the text in the paragraph
newElement.appendChild(newText);
// Put the paragraph on the end of the document by appending it to
// the body (which is the parent of para)
para.parentNode.appendChild(newElement);
});
Creating a tree
You can create the tree in What is a DOM tree? entirely in JavaScript too.
const root = document.createElement("html");
root.lang = "en";
const head = document.createElement("head");
const title = document.createElement("title");
title.appendChild(document.createTextNode("My Document"));
head.appendChild(title);
const body = document.createElement("body");
const header = document.createElement("h1");
header.appendChild(document.createTextNode("Header"));
const paragraph = document.createElement("p");
paragraph.appendChild(document.createTextNode("Paragraph"));
body.appendChild(header);
body.appendChild(paragraph);
root.appendChild(head);
root.appendChild(body);
Event Propagation
This example demonstrates how events fire and are handled in the DOM in a very simple way. When the BODY of this HTML document loads, an event listener is registered with the top row of the TABLE. The event listener handles the event by executing the function stopEvent, which changes the value in the bottom cell of the table.
However, stopEvent also calls an event object method, event.stopPropagation, which keeps the event from bubbling any further up into the DOM. Note that the table itself has an onclick event handler that ought to display a message when the table is clicked. But the stopEvent method has stopped propagation, and so after the data in the table is updated, the event phase is effectively ended, and an alert box is displayed to confirm this.
<table id="t-daddy">
<tbody>
<tr id="tbl1">
<td id="c1">one</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td id="c2">two</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
#t-daddy {
border: 1px solid red;
}
#c1 {
background-color: pink;
}
function stopEvent(event) {
const c2 = document.getElementById("c2");
c2.textContent = "hello";
// this ought to keep t-daddy from getting the click.
event.stopPropagation();
console.log("event propagation halted.");
}
const elem = document.getElementById("tbl1");
elem.addEventListener("click", stopEvent);
document.getElementById("t-daddy").addEventListener("click", () => {
console.log("t-daddy clicked");
});
Displaying event object properties
This example uses DOM methods to display all the properties of the onload event object and their values in a table. It also shows a useful technique of using a for...in loop to iterate over the properties of an object to get their values.
The properties of event objects differs greatly between browsers, the WHATWG DOM Standard lists the standard properties, however many browsers have extended these greatly.
Put the following code into a blank text file and load it into a variety of browsers, you'll be surprised at the different number and names of properties. You might also like to add some elements in the page and call this function from different event handlers.
<h1>Properties of the DOM <span id="eventType"></span> Event Object</h1>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
thead {
font-weight: bold;
}
td {
padding: 2px 10px;
}
.odd {
background-color: #efdfef;
}
.even {
background-color: white;
}
function showEventProperties(e) {
function addCell(row, text) {
const cell = row.insertCell(-1);
cell.appendChild(document.createTextNode(text));
}
const event = e || window.event;
document.getElementById("eventType").textContent = event.type;
const table = document.createElement("table");
const thead = table.createTHead();
let row = thead.insertRow(-1);
const labelList = ["#", "Property", "Value"];
const len = labelList.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
addCell(row, labelList[i]);
}
const tbody = document.createElement("tbody");
table.appendChild(tbody);
for (const p in event) {
row = tbody.insertRow(-1);
row.className = row.rowIndex % 2 ? "odd" : "even";
addCell(row, row.rowIndex);
addCell(row, p);
addCell(row, event[p]);
}
document.body.appendChild(table);
}
showEventProperties(event);
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| DOM |