PannerNode: refDistance property
Baseline
Widely available
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015.
The refDistance property of the PannerNode interface is a double value representing the reference distance for reducing volume as the audio source moves further from the listener – i.e., the distance at which the volume reduction starts taking effect. This value is used by all distance models.
The refDistance property's default value is 1.
Value
A non-negative number. If the value is set to less than 0, a RangeError is thrown.
Exceptions
RangeError-
Thrown if the property has been given a value that is outside the accepted range.
Examples
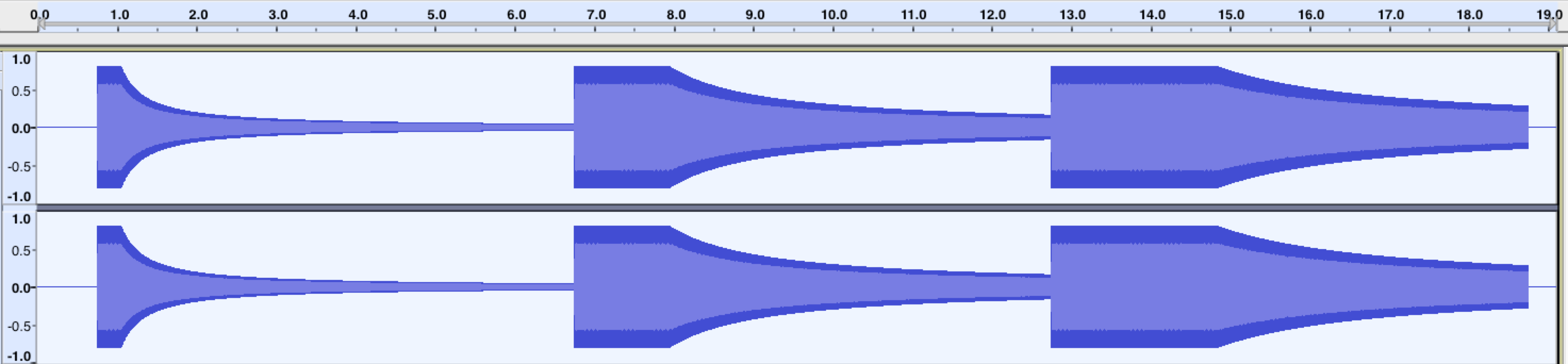
This example demonstrates how different values of refDistance affect how the volume of a sound decays as it moves away from the listener. Unlike rolloffFactor, changing this value also delays the volume decay until the sound moves past the reference point.
const context = new AudioContext();
// all our test tones will last this many seconds
const NOTE_LENGTH = 6;
// this is how far we'll move the sound
const Z_DISTANCE = 20;
// this function creates a graph for the test tone with a given refDistance
// and schedules it to move away from the listener along the Z (depth-wise) axis
// at the given start time, resulting in a decrease in volume (decay)
const scheduleTestTone = (refDistance, startTime) => {
const osc = new OscillatorNode(context);
const panner = new PannerNode(context);
panner.refDistance = refDistance;
// set the initial Z position, then schedule the ramp
panner.positionZ.setValueAtTime(0, startTime);
panner.positionZ.linearRampToValueAtTime(Z_DISTANCE, startTime + NOTE_LENGTH);
osc.connect(panner).connect(context.destination);
osc.start(startTime);
osc.stop(startTime + NOTE_LENGTH);
};
// this tone should decay immediately and fairly quickly
scheduleTestTone(1, context.currentTime);
// this tone should decay slower and later than the previous one
scheduleTestTone(4, context.currentTime + NOTE_LENGTH);
// this tone should decay only slightly, and only start decaying fairly late
scheduleTestTone(7, context.currentTime + NOTE_LENGTH * 2);
After running this code, the resulting waveforms should look something like this:
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| Web Audio API # dom-pannernode-refdistance |