你的第二个 WebExtension
如果你已经阅读了 你的第一个扩展,那么你现在已经知道如何写一个扩展了。在这篇文章,我们将写一个稍微复杂一点点的扩展来为你展示更多的一些 API。
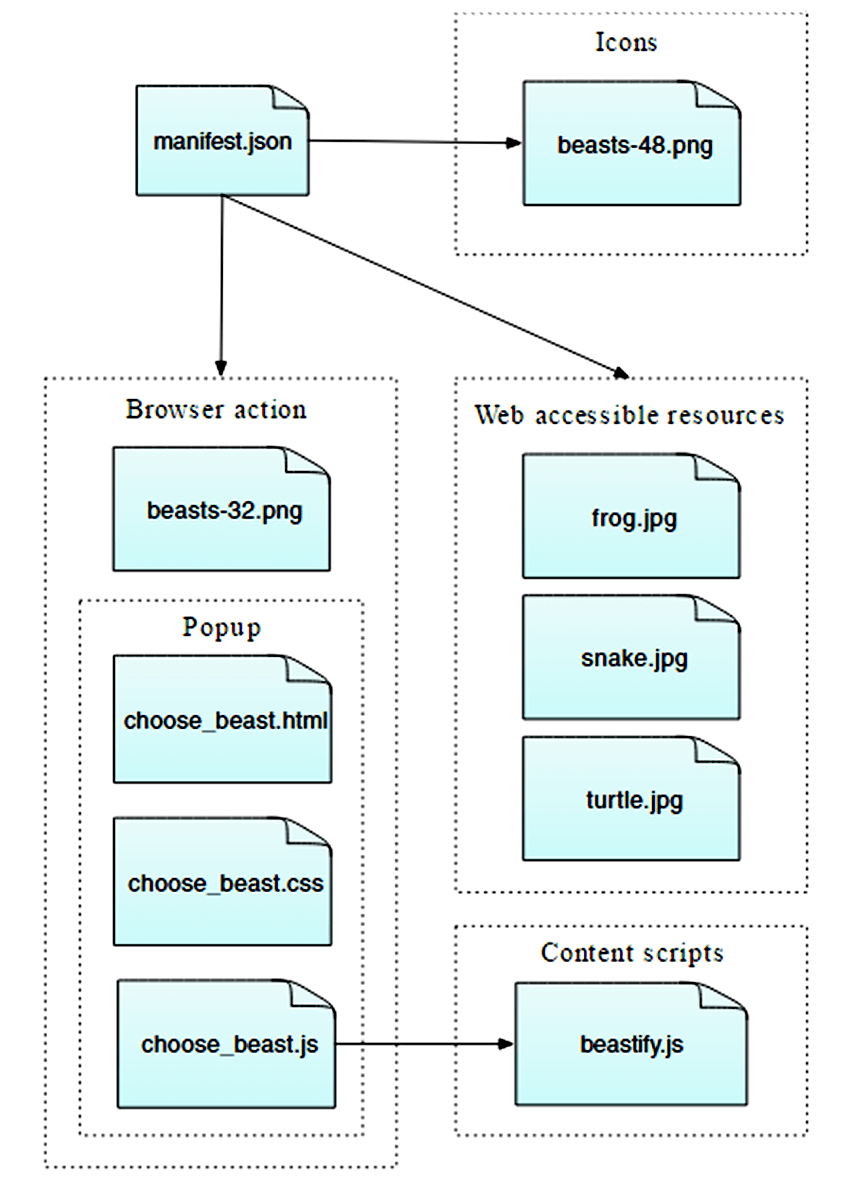
这个扩展会添加一个新按钮到 Firefox 的工具栏。在用户点击该按钮时,我们会显示一个弹出窗(popup)来让他们选择一种动物。在他们选择之后,我们会将当前网页替换为他所选动物的图片。
要实现这点,我们将:
-
定义一个浏览器动作 (browser action),这用来附加一个按钮到 Firefox 的工具栏。 对于该按钮,我们将提供:
- 一个文件名为 "beasts-32.png" 的图标
- 按钮被按下时要打开的弹出窗。该弹出窗将包含 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript。
-
为扩展定义一个图标,叫做“beasts-48.png”。这个将会在 Add-ons 管理器中显示。
-
写一个内容脚本 "beastify.js",用于注入到网页中。 这是用来实际修改页面的代码。
-
打包一些动物的图像,用以替换网页中的图像。 我们让图像成为“Web 可访问资源”(web accessible resources),以便页面可以引用它们。
你可以想象这样的扩展的整体结构:
这是一个非常简单的扩展,但也展示了 WebExtensions API 的许多基本概念:
- 添加一个按钮到工具栏
- 定义一个将使用 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 的弹出窗
- 注入 content scripts 到网页
- content scripts 与扩展的其他部分之间的通信
- 打包你的扩展的资源,使其可被网页所用
你可以在 GitHub 找到该扩展的完整的源代码。
写这个扩展,你需要 45 或更高版本的 firefox。
编写扩展
创建一个新目录,并切换到该目录:
mkdir beastify
cd beastify
manifest.json
现在创建一个名为 "manifest.json" 的文件,并对其添加下列内容:
{
"manifest_version": 2,
"name": "Beastify",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "在工具栏添加一个互动图标。点击按钮选择一个动物,然后当前活动的标签页的内容会被替换成被选择的动物的图片。参见 https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/Add-ons/WebExtensions/Examples#beastify",
"homepage_url": "https://github.com/mdn/webextensions-examples/tree/main/beastify",
"icons": {
"48": "icons/beasts-48.png"
},
"permissions": ["activeTab"],
"browser_action": {
"default_icon": "icons/beasts-32.png",
"default_title": "Beastify",
"default_popup": "popup/choose_beast.html"
},
"web_accessible_resources": [
"beasts/frog.jpg",
"beasts/turtle.jpg",
"beasts/snake.jpg"
]
}
-
最开始的三个属性:
manifest_version,name,version, 是必须的并且包含了插件最基本的信息。 -
description 和 homepage_url 是可选的,但是推荐填写,因为它们提供关于扩展的有用信息。
-
icons 也是可选但推荐的,它决定了插件在附加组件中的图标。
-
permissions列出了插件所需要的权限。在这里我们仅需要 activeTab permission。 -
browser_action指定了工具栏按钮。我们在这里提供了三个信息片段:default_icon是必须的,指定了按钮的图标。default_title是可选的,用于按钮的提示。default_popup在你想要当用户点击按钮时显示出一个弹出窗时使用。而在这里,我们需要,所以我们列入这个键并将其指向扩展中包括的一个 HTML 文件。
-
web_accessible_resources列出了页面可访问的资源。例如由于当前插件使用动物图像替换了页面原有的图像,当前的动物图像要可以被页面访问。
需要注意,所有路径是相对于 manifest.json。
图标
插件应该有一个图标。这个图标被用于显示在附加组件管理器中(可以通过"about:addons"来访问)。当前插件中 manifest.json 指定了我们插件的图标位于"icons/beasts-48.png"。
创建“icons”文件夹,并将图标命名为“beasts-48.png”。你可以使用我们例子中的图标,它是从 Aha-Soft’s Free Retina iconset 截取的,使用需要遵循该网站的许可证。
如果你使用自己的图标,它的尺寸应该是 4848 像素的。同时,对于高分辨率的设备,可以提供 9696 像素的图片。此时,manifest.json 应当这样配置:
"icons": {
"48": "icons/beasts-48.png",
"96": "icons/beasts-96.png"
}
工具栏按钮
工具栏按钮也需要一个图标,并且我们的 manifest.json 承诺我们会为该工具栏在 "icons/beasts-32.png" 提供一个图标。
将一个图标命名为为 "beasts-32.png"并保存到"icons"文件夹。你可以使用例子中的图片,它是取自 IconBeast Lite 图标集并按其许可协议授权使用。
如果你没有弹出窗,用户点击的事件会直接分派到你的插件中。如果你制作了弹出窗,用户点击会直接打开这个弹出窗,而不会被分派给插件。本例中我们需要弹出窗,因此我们现在开始写它。
弹出窗
该弹出窗的函数是让用户选择三种动物的其中一种。
在根目录下创建“popup”文件夹,用于存放弹出窗的代码。弹出窗由以下文件组成:
choose_beast.html定义了界面的主面板choose_beast.css美化内容choose_beast.js通过在当前活跃的标签页中运行内容脚本(content script)处理用户的选择
mkdir popup
cd popup
touch choose_beast.html choose_beast.css choose_beast.js
choose_beast.html
HTML 文件就像这样:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="choose_beast.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="popup-content">
<div class="button beast">Frog</div>
<div class="button beast">Turtle</div>
<div class="button beast">Snake</div>
<div class="button reset">Reset</div>
</div>
<div id="error-content" class="hidden">
<p>Can't beastify this web page.</p>
<p>Try a different page.</p>
</div>
<script src="choose_beast.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
我们有一个 ID 为 "popup-content" 的<div>元素包含了每个动物选择。我们还有另外一个<div> 元素,它的 ID 为 "error-content" ,class 为"hidden"。我们将会使用它以防初始化弹窗的时候出问题。
注意我们引入了 CSS 和 JS 文件,就像网页一样。
choose_beast.css
CSS 固定了弹出窗的大小,确保 3 个选择填充满空间,并给了他们基本点样式。同时隐藏了class="hidden"的元素,这意味着我们的"error-content" <div> 将会被默认隐藏:
html,
body {
width: 100px;
}
.hidden {
display: none;
}
.button {
margin: 3% auto;
padding: 4px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 1.5em;
cursor: pointer;
}
.beast:hover {
background-color: #cff2f2;
}
.beast {
background-color: #e5f2f2;
}
.reset {
background-color: #fbfbc9;
}
.reset:hover {
background-color: #eaea9d;
}
choose_beast.js
我们在弹出窗的脚本中监听点击事件。如果用户选择其中一个动物,我们在当前标签页中插入一段内容脚本。一旦内容脚本加载,我们发送一条有关动物选择的信息:
/**
* CSS to hide everything on the page,
* except for elements that have the "beastify-image" class.
*/
const hidePage = `body > :not(.beastify-image) {
display: none;
}`;
/**
* Listen for clicks on the buttons, and send the appropriate message to
* the content script in the page.
*/
function listenForClicks() {
document.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
/**
* Given the name of a beast, get the URL to the corresponding image.
*/
function beastNameToURL(beastName) {
switch (beastName) {
case "Frog":
return browser.extension.getURL("beasts/frog.jpg");
case "Snake":
return browser.extension.getURL("beasts/snake.jpg");
case "Turtle":
return browser.extension.getURL("beasts/turtle.jpg");
}
}
/**
* Insert the page-hiding CSS into the active tab,
* then get the beast URL and
* send a "beastify" message to the content script in the active tab.
*/
function beastify(tabs) {
browser.tabs.insertCSS({ code: hidePage }).then(() => {
let url = beastNameToURL(e.target.textContent);
browser.tabs.sendMessage(tabs[0].id, {
command: "beastify",
beastURL: url,
});
});
}
/**
* Remove the page-hiding CSS from the active tab,
* send a "reset" message to the content script in the active tab.
*/
function reset(tabs) {
browser.tabs.removeCSS({ code: hidePage }).then(() => {
browser.tabs.sendMessage(tabs[0].id, {
command: "reset",
});
});
}
/**
* Just log the error to the console.
*/
function reportError(error) {
console.error(`Could not beastify: ${error}`);
}
/**
* Get the active tab,
* then call "beastify()" or "reset()" as appropriate.
*/
if (e.target.classList.contains("beast")) {
browser.tabs
.query({ active: true, currentWindow: true })
.then(beastify)
.catch(reportError);
} else if (e.target.classList.contains("reset")) {
browser.tabs
.query({ active: true, currentWindow: true })
.then(reset)
.catch(reportError);
}
});
}
/**
* There was an error executing the script.
* Display the popup's error message, and hide the normal UI.
*/
function reportExecuteScriptError(error) {
document.querySelector("#popup-content").classList.add("hidden");
document.querySelector("#error-content").classList.remove("hidden");
console.error(`Failed to execute beastify content script: ${error.message}`);
}
/**
* When the popup loads, inject a content script into the active tab,
* and add a click handler.
* If we couldn't inject the script, handle the error.
*/
browser.tabs
.executeScript({ file: "/content_scripts/beastify.js" })
.then(listenForClicks)
.catch(reportExecuteScriptError);
从 96 行开始。只要弹出窗加载完,popup script 就会使用 browser.tabs.executeScript() API 在活跃标签页执行 content script。如果执行 content script 成功,content script 会在页面中一直保持,直到标签被关闭或者用户导航到其他页面。
browser.tabs.executeScript()调用失败的常见原因是你不能在所有页面执行 content scripts。例如,你不能在特权浏览器页面执行,像 about:debugging,你也不能在addons.mozilla.org域执行。如果调用失败,reportExecuteScriptError()会隐藏"popup-content" <div>,并展示"error-content" <div>, 然后打印一个错误到控制台。
如果成功执行 content script,我们会调用 listenForClicks()。这个监听了弹窗上的点击事件。
- 如果点击有
class="beast"的按钮上,将会调用beastify(). - 如果点击有
class="reset"的按钮上,将会调用reset().
beastify() 函数做了三件事:
- 将被点击的按钮映射到一个指向特定动物图片的 URL
- 通过
browser.tabs.insertCSS()API 向页面注入一些 CSS 来隐藏整个页面的内容 - 通过
browser.tabs.sendMessage()API 向 content script 发送“beastify”信息,要求其 beastify 页面,同时向其传递一个指向动物图片的 URL
reset() 函数实际上就是撤销 beastify :
- 通过
browser.tabs.removeCSS()API 移除我们添加的 CSS - 向 content script 发送“reset”信息要求其重置页面
The content script
在扩展的根目录下创建一个新的文件夹,叫做"content_scripts",然后在里面新建一个新的名为 "beastify.js" 的文件,内容如下:
(function () {
/**
* Check and set a global guard variable.
* If this content script is injected into the same page again,
* it will do nothing next time.
*/
if (window.hasRun) {
return;
}
window.hasRun = true;
/**
* Given a URL to a beast image, remove all existing beasts, then
* create and style an IMG node pointing to
* that image, then insert the node into the document.
*/
function insertBeast(beastURL) {
removeExistingBeasts();
let beastImage = document.createElement("img");
beastImage.setAttribute("src", beastURL);
beastImage.style.height = "100vh";
beastImage.className = "beastify-image";
document.body.appendChild(beastImage);
}
/**
* Remove every beast from the page.
*/
function removeExistingBeasts() {
let existingBeasts = document.querySelectorAll(".beastify-image");
for (let beast of existingBeasts) {
beast.remove();
}
}
/**
* Listen for messages from the background script.
* Call "beastify()" or "reset()".
*/
browser.runtime.onMessage.addListener((message) => {
if (message.command === "beastify") {
insertBeast(message.beastURL);
} else if (message.command === "reset") {
removeExistingBeasts();
}
});
})();
content script 做的第一件事是检查全局变量 window.hasRun:如果它被设置了,脚本直接返回,否则设置window.hasRun并继续。原因是每次用户打开弹出窗,弹出窗就会在活跃页面执行一个 content script,所以我们可能会在单个页面运行多个脚本实例。如果是这样的话,我们需要保证只有一个实例在做所有事情。
然后,从第 40 行开始,content script 监听来自弹出窗的信息,使用browser.runtime.onMessage API。在上面我们看到弹出窗脚本能够发送两种不同的信息:"beastify" and "reset"。
- 如果信息是 "beastify",我们期待它包含一个指向动物图片的 URL。我们移除先前调用添加的动物图片,然后构造并添加一个 src 属性被设置动物图片 URL 的
<img>元素。 - 如果信息是 "reset",我们只需要移除所有被添加的动物片。
动物们
最后,我们要加入包含动物们的图像。
创建"beasts"文件夹,之后将图片放入并命名。你可以从 GitHub 仓库或这里下载图片:



测试
请仔细确认项目目录如下所示:
beastify/
beasts/
frog.jpg
snake.jpg
turtle.jpg
content_scripts/
beastify.js
icons/
beasts-32.png
beasts-48.png
popup/
choose_beast.css
choose_beast.html
choose_beast.js
manifest.json
Firefox 45 开始,你可以临时从硬盘中安装扩展
在 Firefox 地址栏中输入:about:debugging,单击“临时载入附加组件”,然后选择你的 manifest.json 文件。
然后你应该已经看到扩展图标出现在了 Firefox 的工具条上:
![]()
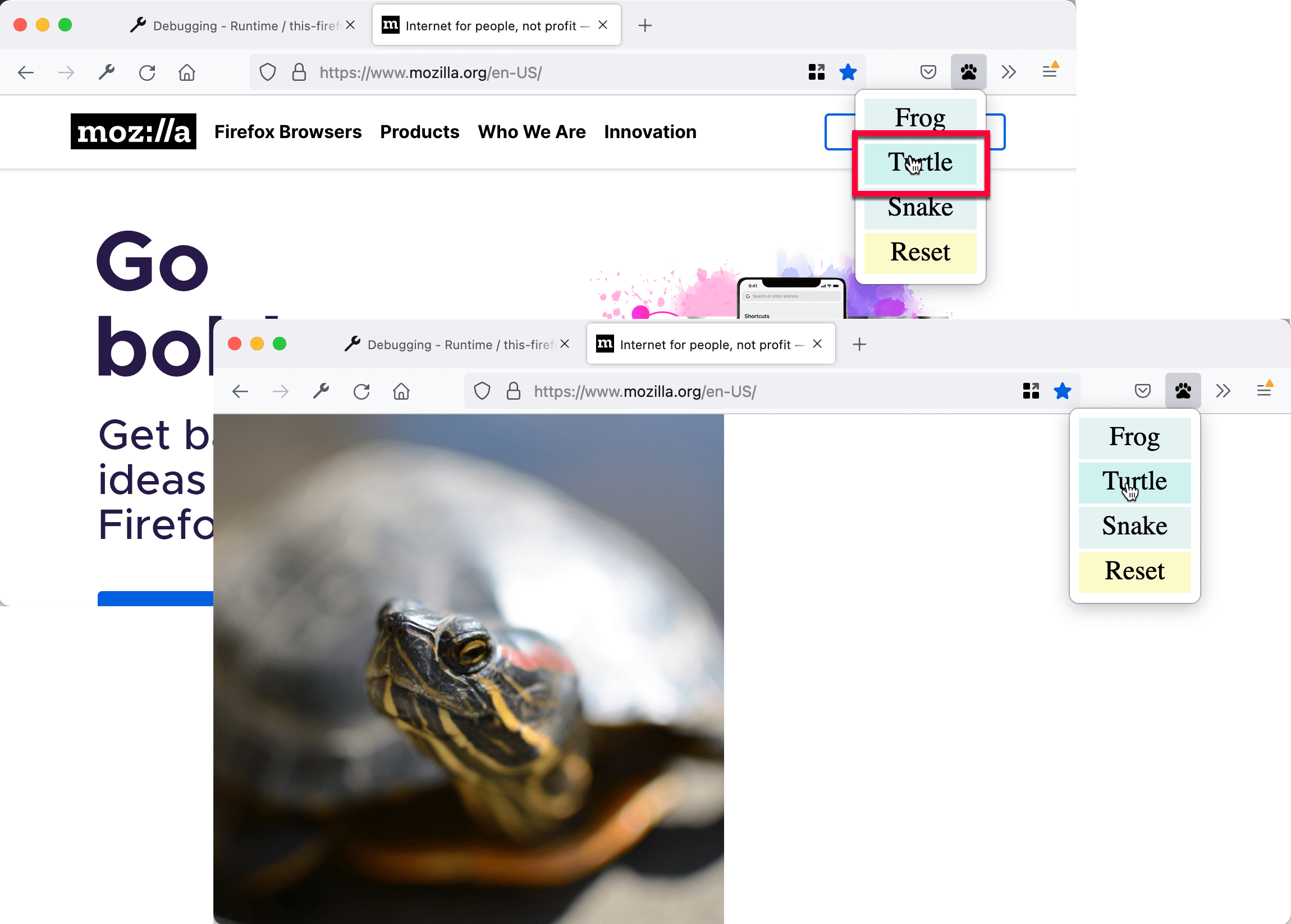
打开一个网页,然后点击图标,选择一个动物,然后观察网页的变化
用命令行开发
你可以通过使用 web-ext 工具来将临时安装的工作自动化,试试这个:
cd beastify
web-ext run
接下来做什么?
你已经创建了一个更加高级的 Firefox Web 扩展,接下来可以: