
Introducing AI Help (Beta): Your Companion for Web Development
Hello, developers!
We're thrilled to announce the latest addition to MDN: AI Help (currently in Beta), developed in collaboration with our partners at Supabase. AI Help is only available to logged-in users, i.e. it requires you to create an MDN Plus account.
AI Help is not just a new tool—it's your new problem-solving companion. It is designed to optimize your search processes, making it quick and easy to find the information you need. Here's how it works: simply ask a question on MDN and AI Help gets to work.
The aim? To streamline your interaction with our website and get you back to coding faster, equipped with the insights you were looking for. We're excited for you to try AI Help and look forward to your feedback on this new feature!
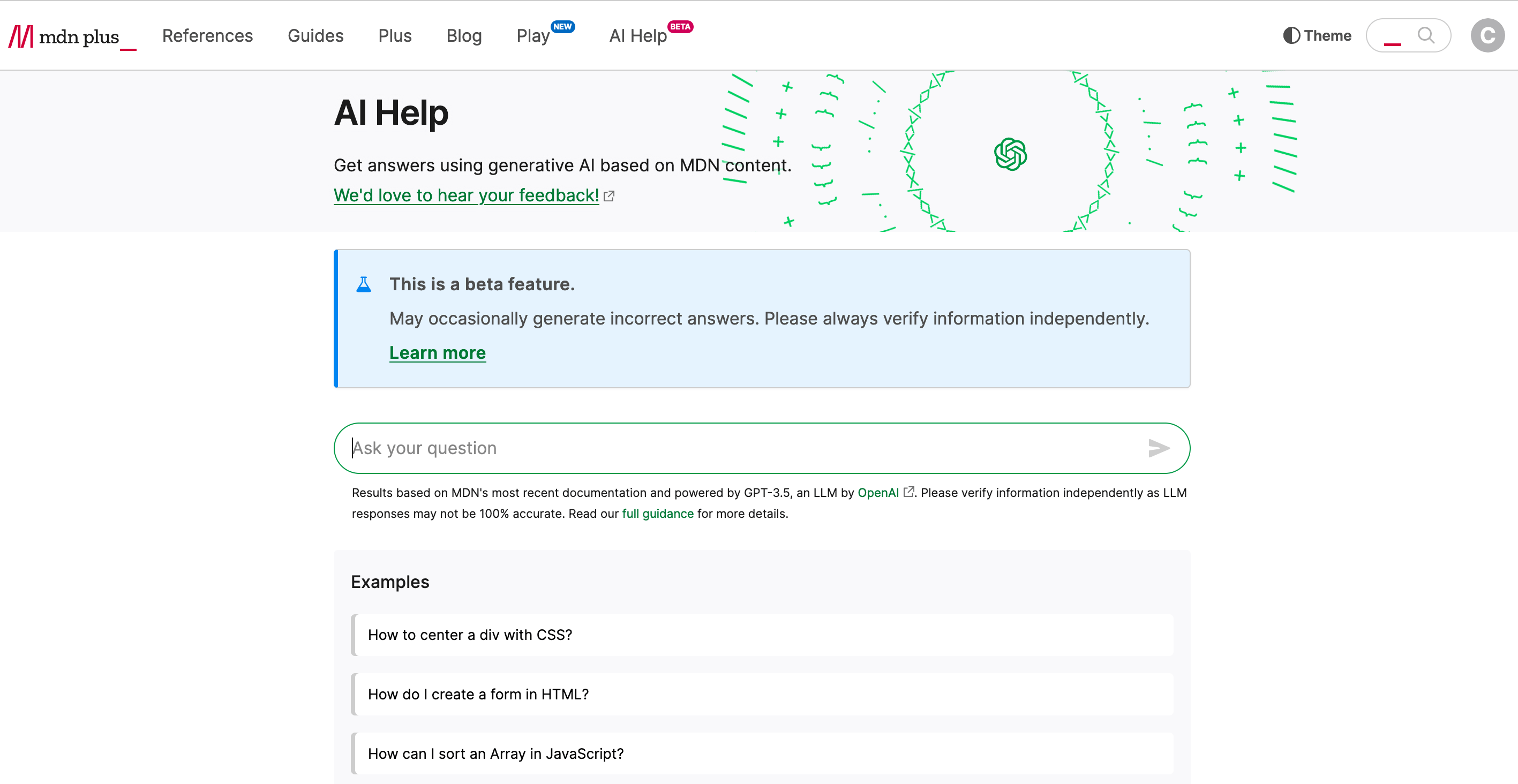
Key features
Quick Access to Knowledge: AI Help connects you to the expansive MDN database, offering quick answers to your queries or coding best practices. The tool is currently limited to the MDN documentation only.
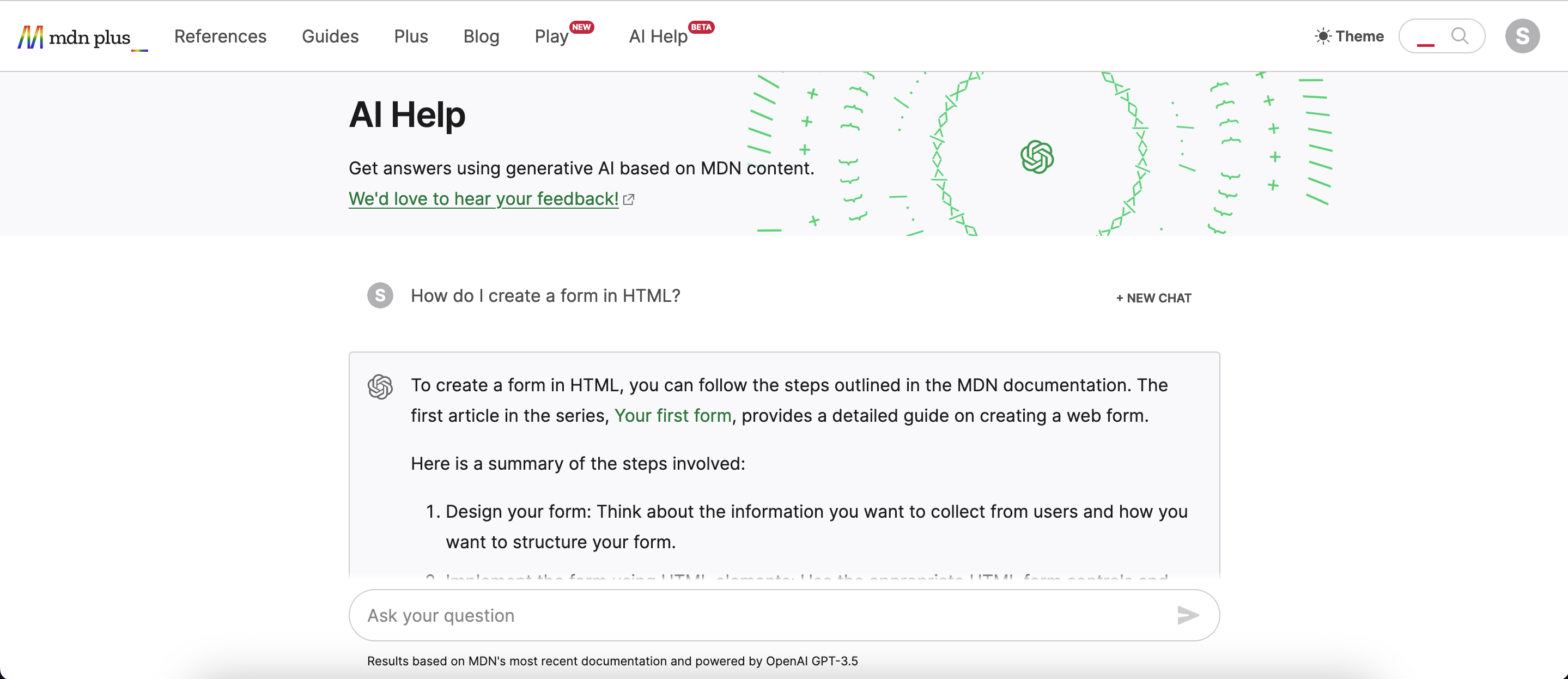
Learning Support: More than a Q&A tool, AI Help offers examples to help you grasp more complex concepts. AI Help also displays links to the articles that were consulted for offering the answer.
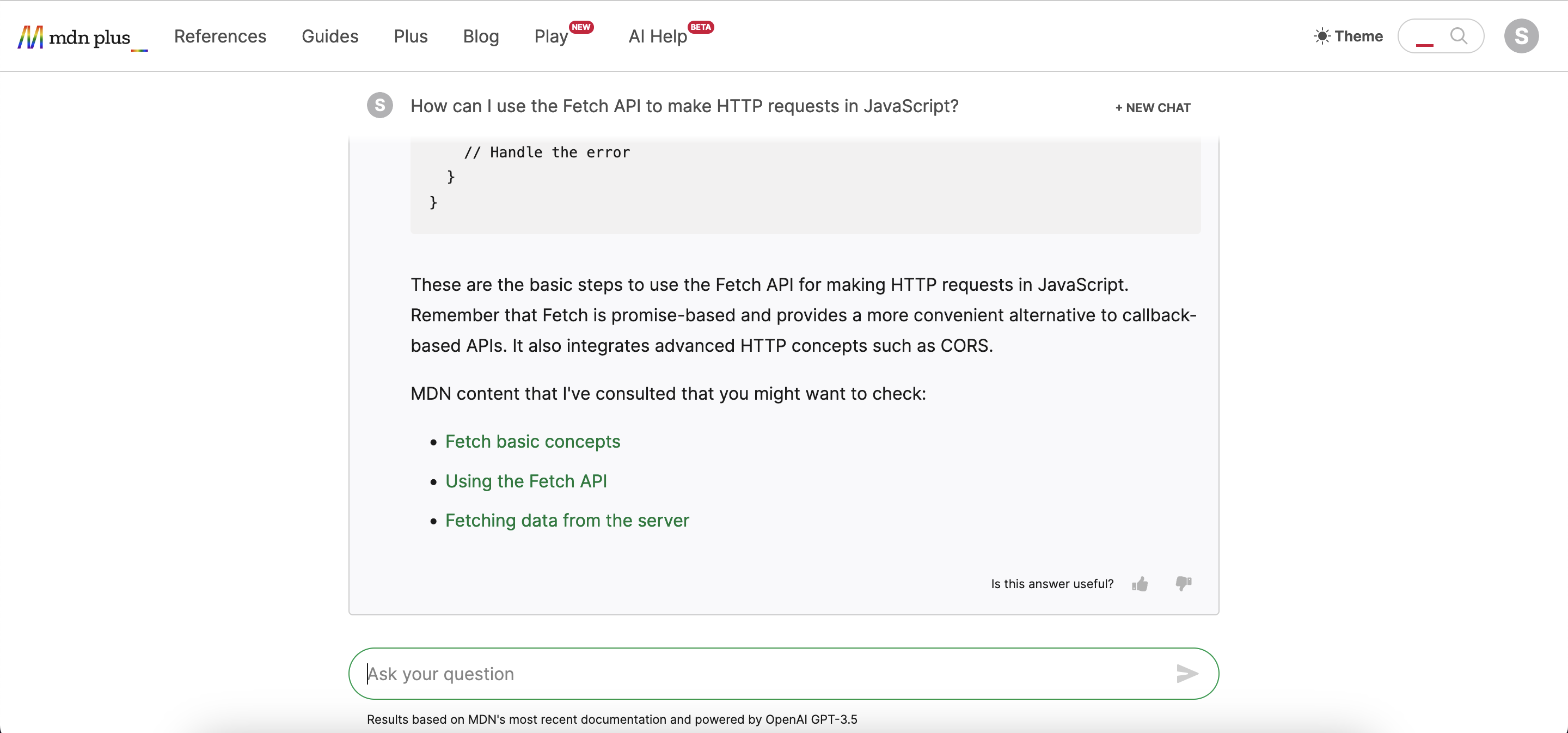
Under the Hood
AI Help leverages two technologies that work well together:
Embeddings for similarity search
Firstly, we generate embeddings for every section of our MDN articles. In the realm of data science, embeddings refer to the transformation of high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space. Each embedding, typically a vector, encapsulates certain characteristics or features of the original data. These embeddings capture both semantic and syntactic relationships among words or sentences, positioning them within a continuous vector space. This placement allows the model to comprehend contextual and relational nuances among the words. For instance, words or sentences bearing similar meanings or those frequently appearing together tend to have proximate vector representations. We store these embeddings in a PostgreSQL database, hosted by Supabase, with the pgvector extension installed. Once we receive a user's question, we generate another embedding for that query. This allows us to perform a similarity search (a distance search in the embedding space) to identify the most relevant sections within the MDN.
Adding Generative AI
Having identified a question and the related content, we can then streamline the process of finding an answer. Instead of making the user read all the content and extract an answer themselves, we utilize OpenAI's Chat API to craft a prompt. This prompt includes several system-level instructions about the desired tone and other related considerations, along with more technical guidelines, such as the requirement to always reply in markdown. We then use the previously related content as a context for the Chat API and ask the user's question on their behalf. This process enables a more efficient interaction, leveraging AI to help users access the information they need.
We invite you to try it today and see the difference it can make. Just create a free MDN Plus account to get started. Please keep in mind that we are launching this feature in Beta: some answers can be incomplete or wrong, and we strongly encourage you to also check the MDN article links that we'll provide. As we refine this feature, we look forward to delivering faster, more accurate responses, and an even better user experience. Your feedback is critical to our progress, helping us tailor AI Help to better meet your needs.
Thank you for being a part of this exciting step forward. Together, let's revolutionize the web development journey. Create a free MDN Plus account today!
*Find out more about Supabase Clippy, that we have used as inspiration for our own integration.
Updated July 8th: Updated blog post to avoid setting wrong expectations. Added clarifications about the feature being beta and only available to logged-in users.