HTMLElement: offsetHeight property
Baseline
Widely available
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015.
The offsetHeight read-only property of the HTMLElement interface returns the height of an element, including vertical padding and borders, as an integer.
Typically, offsetHeight is a measurement in pixels of the element's CSS height, including any borders, padding, and horizontal scrollbars (if rendered). It does not include the height of pseudo-elements such as ::before or ::after. For the document body object, the measurement includes total linear content height instead of the element's CSS height. Floated elements extending below other linear content are ignored.
If the element is hidden (for example, by setting style.display on the element or one of its ancestors to "none"), then 0 is returned.
Value
An integer.
Examples
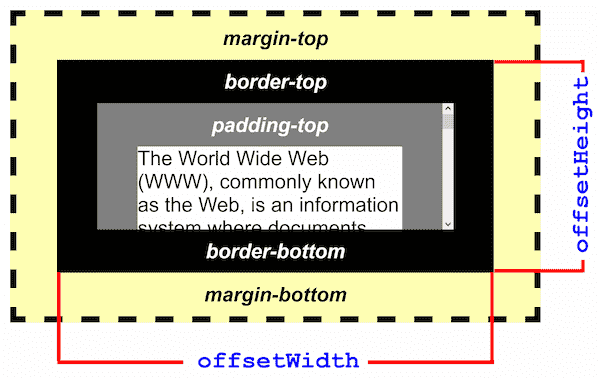
The example image above shows a scrollbar and an offsetHeight which fits on the window. However, non-scrollable elements may have large offsetHeight values, much larger than the visible content. These elements are typically contained within scrollable elements; consequently, these non-scrollable elements may be completely or partly invisible, depending on the scrollTop setting of the scrollable container.
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| CSSOM View Module # dom-htmlelement-offsetheight |
Browser compatibility
Loading…